Have you ever clocked in for a shift, only to find your desk replaced by a whirring metal arm? Or sat through a meeting where a monotone voice delivered a presentation you could have sworn you wrote? The age of the robots is upon us, and the question on everyone’s mind is no longer science fiction: will robots take MY job? Buckle up, because this article dives headfirst into the thrilling automation revolution, exploring the battle lines between human and machine. We’ll uncover the jobs most at risk of extinction, chart a course for the careers likely to thrive, and equip you with the skills to not just survive, but dominate in this age of whirring gears and artificial intelligence. So, is your resume robot-proof? Read on and find out!
To answer the question “will robots take my job“, first we have to understand what is automation and robotics. Let’s find out.
Automation and Robotics
Automation is the technology of employing machines to complete jobs that were previously performed by people. This can encompass both physical duties, like constructing vehicles on a factory assembly line, and intellectual ones, like assessing essays or trading stocks. Automation can help to increase efficiency, accuracy, and consistency.

Robotics is the branch of engineering that studies the design, manufacture, operation, and use of robots. Robots are robots that detect their surroundings and respond accordingly. They may be programmed to execute a variety of activities, ranging from simple repetitive operations to complicated jobs requiring precision and intelligence.
Reference: Read Scholarly article about Automation and Robotics
Example of Automation and Robotics
Imagine a bustling coffee shop where, alongside the familiar hum of the espresso machine, there’s a whirring dance of robotic arms. Enter the Barista Bot, a marvel of automation and robotics working in perfect harmony.
Automation:
- The Barista Bot is programmed with precise coffee-making algorithms.
- It automatically grinds the perfect amount of beans based on your chosen drink.
- Sensors ensure the correct water temperature and pressure are used for optimal extraction.
Robotics:
- The robotic arms move with dexterity, mimicking the motions of a skilled barista.
- They precisely tamp the grounds, steam the milk to a silky consistency, and pour latte art with impressive finesse.
- Cameras and sensors allow the robot to adjust for different cup sizes and preferences.
The Result:
The Barista Bot delivers a consistently delicious cup of coffee, every time. While it may lack the personal touch of a human barista’s conversation, it frees them up for more complex tasks like creating specialty drinks or interacting with customers. This is a prime example of how automation and robotics can work together, enhancing efficiency and productivity without sacrificing quality.
Growing Concerns About Job Displacement by Robots
Millions of jobs across various industries, from manufacturing to transportation, are susceptible to automation. Repetitive tasks, data analysis, and even some customer service interactions can now be performed more efficiently by machines. This raises a real question about the future of work and the potential for widespread job displacement.
The fear factor
The specter of robot-induced unemployment is a scary one. People worry about their ability to support themselves and their families, and the social and economic consequences of mass job loss. The anxiety is fueled by news reports and studies highlighting the potential for millions of jobs to be replaced by automation in the coming decades.
But is it all doom and gloom?
The story isn’t entirely bleak. While some jobs will undoubtedly be lost, automation also creates new opportunities. As machines take over the repetitive tasks, humans will be needed for higher-level skills like creativity, problem-solving, and critical thinking. New jobs will emerge in fields like robotics engineering, data science, and cybersecurity – areas that require a different skillset than those being automated.
What is the key to survival?
The future of work will likely involve a more collaborative approach between humans and machines. The key to success will be adaptability and a willingness to learn new skills. Investing in education and training programs that equip individuals for the jobs of tomorrow will be crucial.
So, are robots coming for your job?
It’s a complex issue with no easy answer. While automation poses a challenge, it also presents an opportunity for a workforce transformation. By embracing lifelong learning and focusing on uniquely human skills, we can navigate this technological shift and ensure a future where humans and machines work together to build a better tomorrow.
Historical Context of Automation and Robotics
The desire to make things automatic and create machines that can do our work isn’t new. It goes way back! Here’s a simplified look at how automation and robotics developed:
Ancient Inventions:
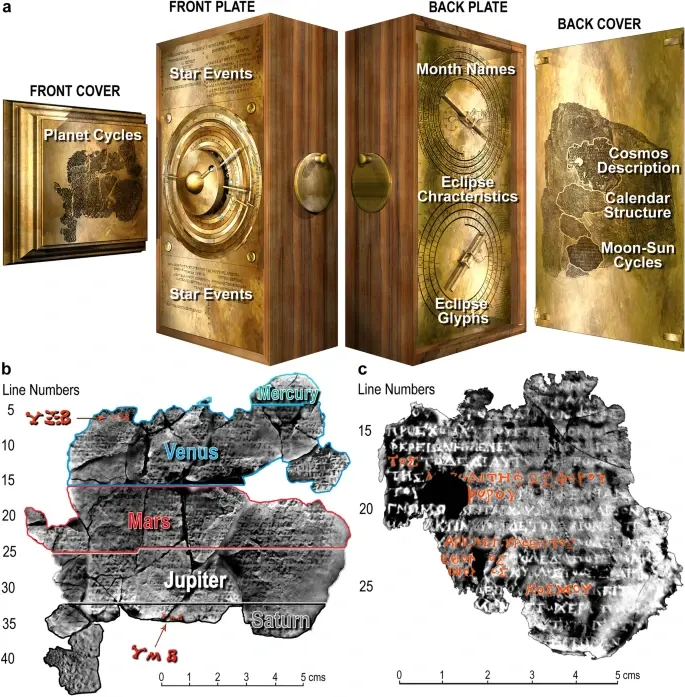
Even back in ancient Greece, people were tinkering with automation. The Antikythera mechanism, a super cool gadget for tracking the stars, is a great example of an early robot.
Leonardo da Vinci’s Ideas
This famous inventor wasn’t just about art. He sketched out ideas for all sorts of machines that could work by themselves, including a metal knight!
The Industrial Revolution (1700s-1800s)
This period saw a big jump in automation. Factories started using steam engines and power looms to do tasks that people used to do by hand. This made things a lot faster and more efficient.
Early Robots (1900s)
The 1900s brought even more advancements. In the 1940s, William Grey Walter created the first robots that could move around on their own and react to their surroundings.
Industrial Robots Take Off (1950s):
In 1954, a guy named George Devol invented a game-changer: the Unimate. This was basically the first industrial robot, a machine with an arm that could be programmed to do specific tasks in factories.
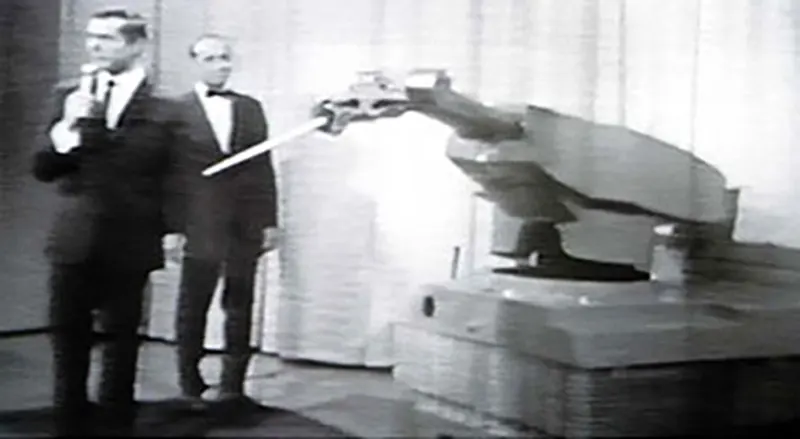

Robots on the Assembly Line:
By the later part of the 1900s, robots became more common in factories, especially car factories. They were initially used for repetitive jobs like welding and painting.
Artificial Intelligence Steps In (Late 1900s):
The development of Artificial Intelligence (AI) gave robots a major boost. With AI, robots became smarter and able to handle more complex tasks and situations.
Automation and robotics are constantly evolving, and they’re being used in more and more places besides factories. The future promises even more exciting developments!
Current State of Automation
Automation is booming! It’s no longer just about robots on factory assembly lines. Here’s a glimpse into the current state of automation:
- Wide-spread Adoption: Across industries, businesses are embracing automation to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and boost productivity.
- Beyond Repetitive Tasks: While automation excels at repetitive tasks, it’s also tackling more complex ones. Thanks to Artificial Intelligence (AI), machines can now handle tasks like data analysis, customer service interactions, and even some aspects of creative content generation.
- Increased Investment: Companies are recognizing the value of automation and are investing heavily in automation technologies like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and AI-powered software.
- Rise of the “Digital Workforce”: Many companies have a significant “digital workforce” consisting of software robots and AI assistants that handle tasks previously done by humans.
Statistics on Job Displacement
Here’s a look at some statistics on job displacement due to automation:
Actual Displacement:
- Recent Impact: Data from Socius suggests around 14% of workers have already experienced job displacement due to automation or AI (SEO.ai, 2024). This indicates the current impact might be less severe than initial fears.
Potential Displacement:
- Expert Predictions: Studies like McKinsey’s research project that automation could displace 83 million jobs globally by 2025, while creating 69 million new ones (Statista, 2023). This highlights the potential for job churn.
- Vulnerable Sectors: Office and administrative support tasks are most susceptible, with an automation potential of around 46% (Statista, 2023). Legal tasks (44%) and manufacturing jobs (around 25%) also face significant risks.
Additional Considerations:
- Upskilling and Reskilling: The human capital hub reports that over 54% of workers will require significant reskilling or upskilling by 2022 (The Human Capital Hub, 2024). This emphasizes the need for adaptation.
- Education and Experience: Less educated workers and those in manual labor positions might face greater challenges compared to their highly educated counterparts (PwC UK, n.d.).
It’s important to note that these are just statistics, and the actual impact of automation on jobs will likely vary depending on several factors.
Potential Impacts on Employment
The rise of automation has a double-edged sword effect on employment. Here’s a breakdown of the potential impacts:
Positive Impacts:

- Increased Productivity: Automation can handle repetitive tasks more efficiently, freeing up human workers to focus on higher-value activities that require creativity, problem-solving, and strategic thinking. This can lead to increased productivity and economic growth.
- Improved Quality and Accuracy: Machines excel at performing tasks with high precision and consistency, minimizing errors and improving quality control in various processes.
- 24/7 Operations: Automated systems can operate continuously without breaks or downtime, leading to increased production output.
- Cost Reduction: While there’s an initial investment in automation technologies, the long-term benefits like increased efficiency and fewer errors can lead to significant cost savings for companies.
Negative Impacts:

- Job Displacement: A major concern is that automation might replace human jobs, particularly those involving repetitive tasks. This could lead to unemployment and economic hardship for displaced workers. Sectors like manufacturing, administrative support, and data entry could be significantly affected.
- Skills Gap: As technology evolves, the job market will demand a different skill set. The current workforce might need to adapt and develop new skills (upskilling) or learn entirely new skillsets (reskilling) to stay relevant in the face of automation.
- Ethical Considerations: Bias in AI algorithms and the potential for widespread job displacement raise ethical concerns. We need to ensure fair and responsible implementation of automation to minimize negative social impacts.
Automation is transforming the way we work. While there are job displacement risks, automation also offers significant potential for improving productivity, efficiency, and innovation across various industries.
Automation presents a complex landscape with both exciting possibilities and ethical dilemmas. Let’s delve into three key areas:
Ethical Implications of Automation:
- Bias in AI: Algorithmic bias can perpetuate discrimination in areas like hiring, loan approvals, and criminal justice. We need to ensure fairness and transparency in the development and deployment of AI systems.
- Job Displacement: Automation replacing jobs raises ethical concerns about unemployment, income inequality, and the impact on individuals and families. Companies have a responsibility to plan for workforce transitions and offer support to displaced workers.
- Human Control vs. Machine Control: Autonomous systems raise questions about accountability. Who is responsible for accidents or errors caused by AI or robots? Clear guidelines are needed for ethical decision-making in automated systems.
- Privacy Concerns: Increased automation often involves data collection and analysis. Protecting individual privacy and ensuring proper data security are crucial ethical considerations.
Impact on Societal Well-being and Mental Health:
- Unemployment and Inequality: Job displacement due to automation can lead to economic hardship, social unrest, and a widening gap between the rich and the poor. Policies and programs are needed to ensure a just transition for affected workers.
- The Changing Nature of Work: Automation may lead to job insecurity and a sense of alienation from work. Efforts to reskill and upskill the workforce and promote job satisfaction are essential.
- The Future of Work-Life Balance: With 24/7 automation, the lines between work and personal life may blur. Promoting healthy work practices and encouraging breaks are crucial for mental well-being.
- The Impact on Meaningful Work: If machines take over many jobs, how will people find meaning and purpose in their work? We may need to redefine work and explore the concept of a universal basic income.
Equity and Fairness in the Distribution of Benefits and Risks:
- Unequal Access to Benefits: The benefits of automation may not be evenly distributed. Wealthy companies and individuals might benefit more readily from automation technologies, exacerbating existing inequalities.
- The Risk of Job Polarization: Automation might create new jobs but eliminate others. Lower-skilled workers might be disproportionately impacted, leading to job polarization. Policies to bridge the skills gap and ensure opportunities for all are essential.
- Geographical Inequalities: The impact of automation may vary across regions and countries. Developing countries might be more vulnerable to job displacement as they rely heavily on manufacturing. International cooperation is needed to ensure equitable distribution of benefits.
- The Need for Public Discourse: Open discussions are crucial to ensure that the development and deployment of automation technologies are guided by ethical principles and promote fairness for all.
Addressing these ethical and social considerations is vital for ensuring that automation benefits society as a whole, not just a select few. By focusing on responsible development, proactive planning, and a commitment to fairness, we can harness the power of automation for a positive and inclusive future.
Future Outlook
The future of work will likely be a blend of human and machine capabilities. Here are some predictions:
Rise of Human-Machine Collaboration:
Humans and machines will increasingly work together, with each playing to their strengths. Humans will handle complex tasks requiring creativity and strategic thinking, while machines will excel at data analysis, repetitive tasks, and following instructions.
Demand for New Skills
The job market will value skills like critical thinking, problem-solving, adaptability, and strong communication. The ability to work effectively with technology and data will be essential.
Growth in Specific Sectors:
Jobs in areas like data science, cybersecurity, engineering related to automation, and healthcare are expected to see significant growth.
The Gig Economy:
The rise of freelance and contract work might continue, offering more flexibility but potentially less job security.
Emerging Trends in Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics are constantly evolving, with exciting new trends on the horizon:
Cognitive Automation
AI is becoming more sophisticated, allowing robots to handle complex tasks requiring judgment and decision-making, not just following pre-programmed instructions.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
These robots are designed to work safely alongside human workers, assisting with tasks and automating specific processes.
Recap of Key Points
Automation is transforming the workplace, presenting both opportunities and challenges. Here’s a quick recap:
- Automation can increase productivity, efficiency, and innovation.
- Job displacement due to automation is a concern, but the impact might not be as severe as initially feared.
- The future of work will likely involve human-machine collaboration, demanding new skill sets for the workforce.
- By focusing on continuous learning, transferable skills, and staying adaptable, individuals can thrive in a changing workforce.
The future of work is uncertain, but by proactively addressing these changes, we can ensure that automation benefits both businesses and workers. This will pave the way for a more prosperous and innovative future for all.